表格和数据
表是存储数据的地方。
表格类似于Excel电子表格。它们包含列和行。
例如,这个表有3列(id, name, description)和4行的数据:
id | name | description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The Phantom Menace | Two Jedi escape a hostile blockade to find allies and come across a young boy who may bring balance to the Force. |
| 2 | Attack of the Clones | Ten years after the invasion of Naboo, the Galactic Republic is facing a Separatist movement. |
| 3 | Revenge of the Sith | As Obi-Wan pursues a new threat, Anakin acts as a double agent between the Jedi Council and Palpatine and is lured into a sinister plan to rule the galaxy. |
| 4 | Star Wars | Luke Skywalker joins forces with a Jedi Knight, a cocky pilot, a Wookiee and two droids to save the galaxy from the Empire's world-destroying battle station. |
它与电子表格有一些重要的区别,但如果你是关系型数据库的新手,它是一个很好的学习起点。
创建表
当创建一个表时,最好的做法是同时添加列。
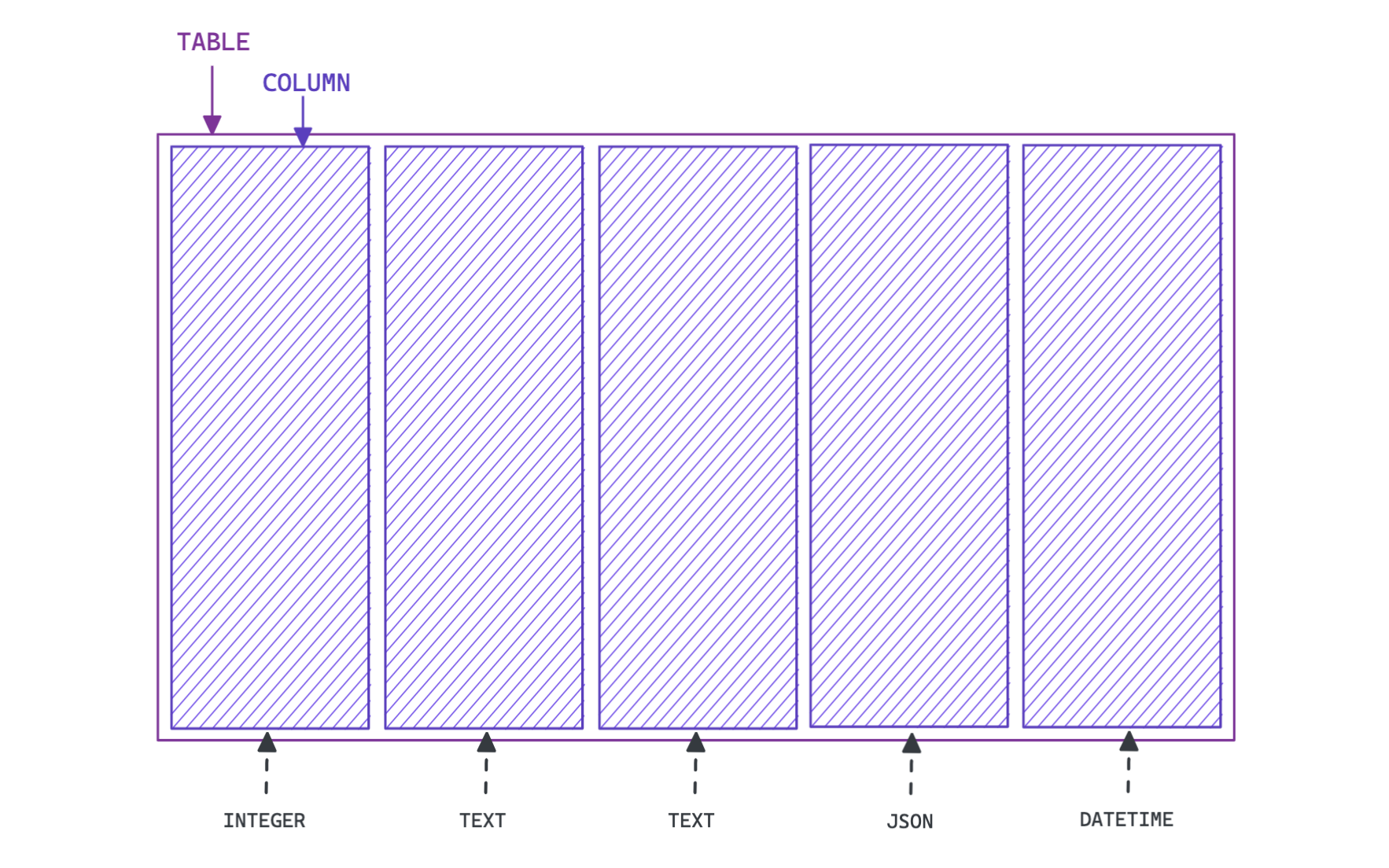
你必须在创建每一列时定义它的 "数据类型"。你可以在创建表后随时添加和删除列。
Supabase 为创建表提供了几个选项。你可以使用仪表板或直接使用 SQL 创建它们。 我们在 Dashboard 中提供了一个 SQL 编辑器,或者你可以 连接到你的数据库并自己运行SQL查询。
- 进入仪表板中的表编辑器页面。
- 单击新表,创建一个名为
todos的表。 - 单击保存。
- 点击新列,创建一个名为
task的列,数据类型为text。 - 单击保存。
note
当命名表时,使用小写字母和下划线而不是空格(例如,table_name,而不是Table Name)。
列
当你创建一个列时,你必须定义 "数据类型"。
数据类型
每个列都是一个预定义的类型。PostgreSQL提供了许多默认类型,你甚至可以设计你自己的(或使用扩展) 如果默认类型不满足你的需求。
显示/隐藏默认数据类型
名称 | 别名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| bigint | int8 | signed eight-byte integer |
| bigserial | serial8 | autoincrementing eight-byte integer |
| bit | fixed-length bit string | |
| bit varying | varbit | variable-length bit string |
| boolean | bool | logical Boolean (true/false) |
| box | rectangular box on a plane | |
| bytea | binary data (“byte array”) | |
| character | char | fixed-length character string |
| character varying | varchar | variable-length character string |
| cidr | IPv4 or IPv6 network address | |
| circle | circle on a plane | |
| date | calendar date (year, month, day) | |
| double precision | float8 | double precision floating-point number (8 bytes) |
| inet | IPv4 or IPv6 host address | |
| integer | int, int4 | signed four-byte integer |
| interval [ fields ] | time span | |
| json | textual JSON data | |
| jsonb | binary JSON data, decomposed | |
| line | infinite line on a plane | |
| lseg | line segment on a plane | |
| macaddr | MAC (Media Access Control) address | |
| macaddr8 | MAC (Media Access Control) address (EUI-64 format) | |
| money | currency amount | |
| numeric | decimal | exact numeric of selectable precision |
| path | geometric path on a plane | |
| pg_lsn | PostgreSQL Log Sequence Number | |
| pg_snapshot | user-level transaction ID snapshot | |
| point | geometric point on a plane | |
| polygon | closed geometric path on a plane | |
| real | float4 | single precision floating-point number (4 bytes) |
| smallint | int2 | signed two-byte integer |
| smallserial | serial2 | autoincrementing two-byte integer |
| serial | serial4 | autoincrementing four-byte integer |
| text | variable-length character string | |
| time [ without time zone ] | time of day (no time zone) | |
| time with time zone | timetz | time of day, including time zone |
| timestamp [ without time zone ] | date and time (no time zone) | |
| timestamp with time zone | timestamptz | date and time, including time zone |
| tsquery | text search query | |
| tsvector | text search document | |
| txid_snapshot | user-level transaction ID snapshot (deprecated; see pg_snapshot) | |
| uuid | universally unique identifier | |
| xml | XML data |
你可以将列从一种类型变更到另一种类型,但是不同类型之间可能有一些不兼容的地方。例如,如果你把一个时间戳转换到一个日期,你将失去所有以前保存的时间信息。
主键
一个表可以有一个"主键"--每行数据的唯一标识符。关于主键的一些提示:
- 建议为你数据库中的每张表都创建一个主键。
- 你可以使用任何列作为主键,只要它对每行都是唯一的。
- 通常使用
uuid类型或编号的identity列作为主键。
1create table movies ( 2 id bigint generated always as identity primary key 3);
在上面的例子中,我们已经:
1.创建了一个名为id的列;
- 指定数据类型为
bigint; - 指示数据库,这应该是
generated always as identity,这意味着Postgres将自动给这个列分配一个唯一的数字。 - 因为它是唯一的,我们也可以用它作为我们的`主键'。
我们也可以使用`generated by default as identity,这将允许我们插入我们自己的唯一值。
1create table movies ( 2 id bigint generated by default as identity primary key 3);
加载数据
有几种方法可以在Supabase中加载数据。你可以直接向数据库加载数据,或者使用API。 如果你要加载大型数据集,请使用 "批量加载 "说明。
基本数据加载
1insert into movies 2 (name, description) 3values 4 ('The Empire Strikes Back', 'After the Rebels are brutally overpowered by the Empire on the ice planet Hoth, Luke Skywalker begins Jedi training with Yoda.'), 5 ('Return of the Jedi', 'After a daring mission to rescue Han Solo from Jabba the Hutt, the Rebels dispatch to Endor to destroy the second Death Star.');
批量数据加载
当插入大型数据集时,最好使用PostgreSQL的COPY命令。 这可以直接从一个文件加载数据到一个表中。有几种文件格式可用于复制数据:文本、csv、二进制、JSON等。
例如,如果你想把一个CSV文件加载到你的movies数据表中。
./movies.csv1"The Empire Strikes Back", "After the Rebels are brutally overpowered by the Empire on the ice planet Hoth, Luke Skywalker begins Jedi training with Yoda." 2"Return of the Jedi", "After a daring mission to rescue Han Solo from Jabba the Hutt, the Rebels dispatch to Endor to destroy the second Death Star."
你将连接到你的数据库,然后用COPY命令加载文件:
psql -h DATABASE_URL -p 5432 -d postgres -U postgres \ -c "COPY movies FROM './movies.csv';"
用外键连接表
多张表可以用外键 "连接 "在一起。
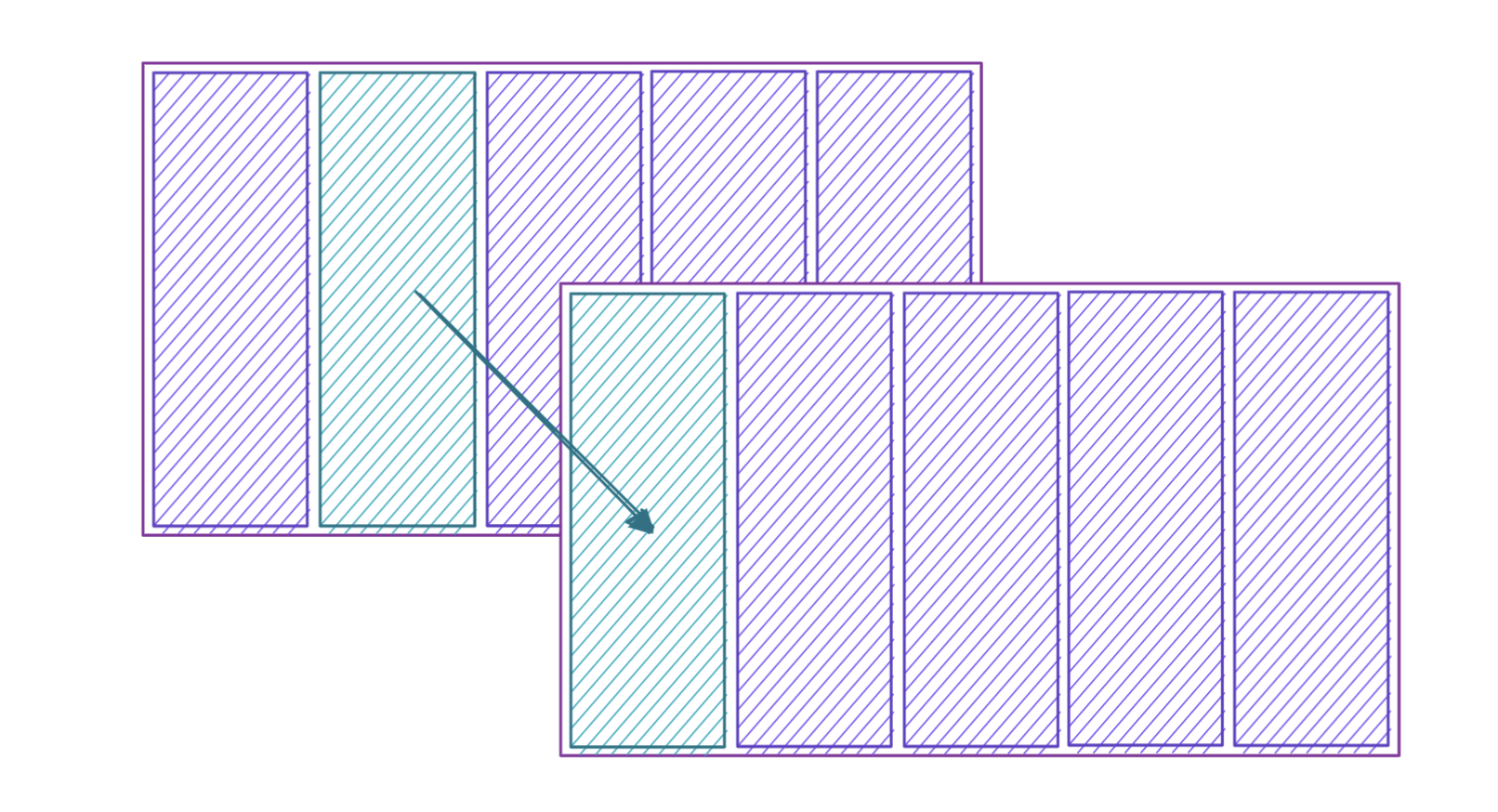
这就是 关系型命名的由来,因为数据通常形成某种关系。
在我们上面的movies例子中,我们可能想为每部电影添加一个 category(例如,"动作片",或 "纪录片")。
让我们创建一个名为 categories的新表,并 连接我们的 movies表。
1create table categories ( 2 id bigint generated always as identity primary key, 3 name text -- category name 4); 5 6alter table movies 7 add column category_id bigint references categories;
你也可以通过创建一个 连接表来创建 多对多关系。
例如,如果你有以下情况。
- 你有一个
movies的列表。 - 一部电影可以有几个
actors。 - 一个
actors可以在几部电影中演出。
Schemas#
表属于schemas。schemas是组织你的表的一种方式,通常是出于安全原因。
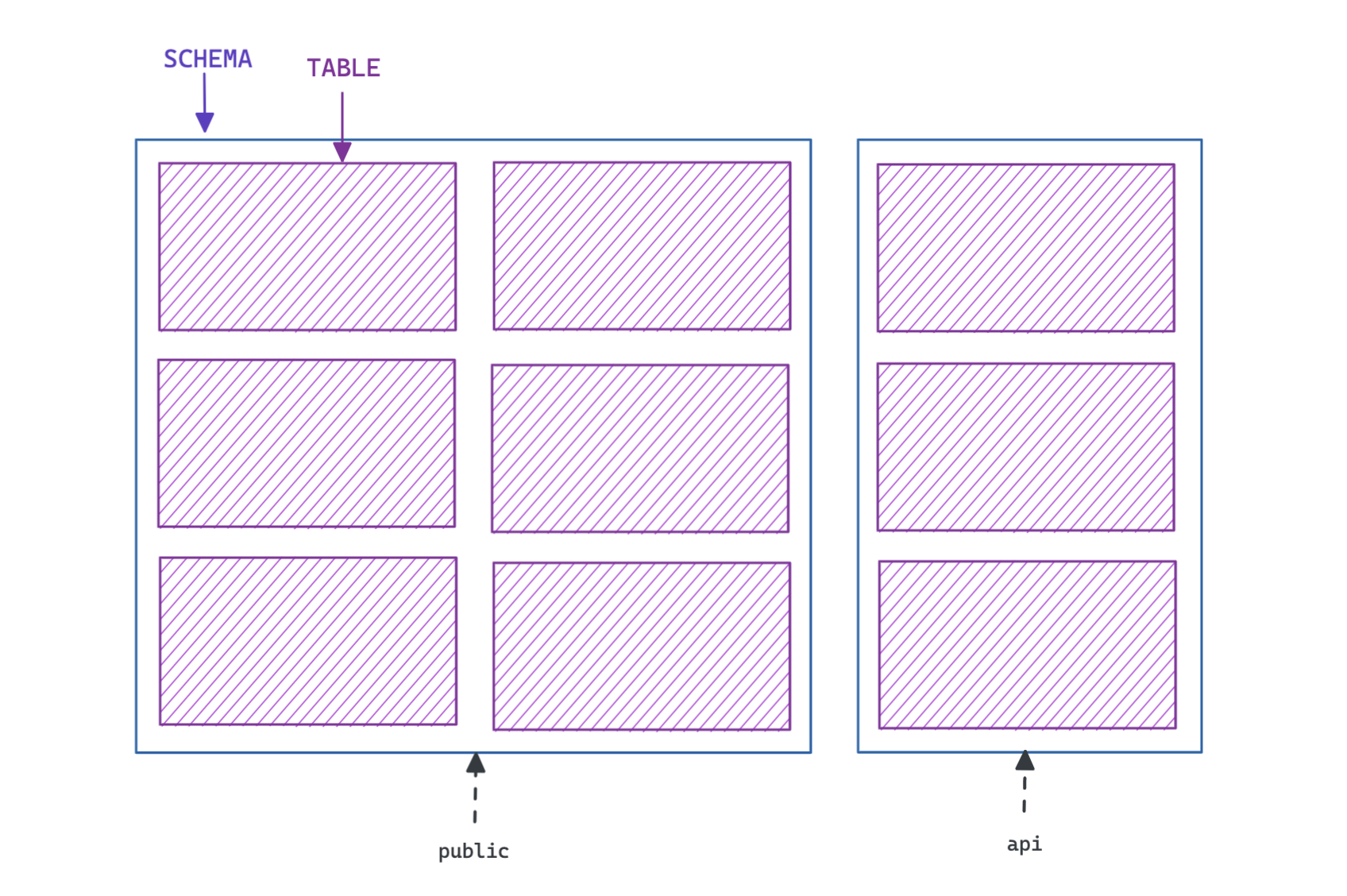
如果你在创建表时没有明确地传递模式,Postgres会假定你想在public模式中创建表。
我们可以创建用于组织表的模式。例如,我们可能希望有一个私人模式,从我们的API中隐藏起来:
1create schema private;
现在我们可以在private模式中创建表:
1create table salaries ( 2 id bigint generated by default as identity primary key, 3 salary bigint not null, 4 actor_id bigint not null references public.actors 5);
视图
视图是查询的一个方便的快捷方式。创建一个视图并不涉及新的表或数据。当运行时,一个底层查询被执行,将其结果返回给用户。
caution
默认情况下,PostgreSQL视图会绕过行级安全,除非你改变它们的所有者(详见: https://github.com/supabase/supabase/discussions/901) PostgreSQL v15(即将推出)将通过security invoker views 对此有一个更直观的控制,前面的步骤就不需要了。
假设我们有一个大学的数据库中的以下表格:
students
| id | name | type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Princess Leia | undergraduate |
| 2 | Yoda | graduate |
| 3 | Anakin Skywalker | graduate |
courses
| id | title | code |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Introduction to Postgres | PG101 |
| 2 | Authentication Theories | AUTH205 |
| 3 | Fundamentals of Supabase | SUP412 |
grades
| id | student_id | course_id | result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | B+ |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | A+ |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | A |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | A- |
| 5 | 3 | 2 | A |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | B- |
创建一个由所有三个表组成的视图将看起来像这样:
1create view transcripts as
2 select
3 students.name,
4 students.type,
5 courses.title,
6 courses.code,
7 grades.result
8 from grades
9 left join students on grades.student_id = students.id
10 left join courses on grades.course_id = courses.id;
11
12alter view transcripts owner to authenticated;
完成后,我们现在可以通过以下方式访问查询:
1select * from transcripts;
何时使用视图
视图提供了几个好处:
- 简单性
- 一致性
- 逻辑上的组织
- 安全性
简单化
当一个查询变得复杂时,调用它就变得很麻烦了。特别是当我们定期运行它时。在上面的例子中,与其反复运行。
1select
2 students.name,
3 students.type,
4 courses.title,
5 courses.code,
6 grades.result
7from grades
8left join students on grades.student_id = students.id
9left join courses on grades.course_id = courses.id;
我们可以运行如下命令来替代:
1select * from transcripts;
此外,视图的行为就像一个典型的表。我们可以安全地在表JOIN中使用它,甚至可以使用现有的视图创建新的视图。
一致性
视图可以确保在重复执行查询时,出错的可能性会减少。在我们上面的例子中,我们可能决定要排除Introduction to Postgres这一课程。该查询将变成:
1select
2 students.name,
3 students.type,
4 courses.title,
5 courses.code,
6 grades.result
7from grades
8 left join students on grades.student_id = students.id
9 left join courses on grades.course_id = courses.id
10where courses.code != 'PG101';
如果没有视图,我们将需要进入每个依赖性查询来添加新的规则。这将增加错误和不一致的可能性,同时也会给开发人员带来很多麻烦。有了视图,我们可以只改变transcripts视图中的基础查询脚本。这个改变将应用于所有使用这个视图的应用程序。
逻辑性组织
通过视图,我们可以给我们的查询一个名字。这对于使用同一数据库的团队来说非常有用。与其猜测一个查询应该做什么,一个名字好的视图可以很容易地解释它。 例如,通过查看视图的名称transcripts,我们可以推断出基础查询可能涉及students、courses和grades表。
安全性
视图可以限制呈现给用户的数据的数量和类型。我们不允许用户直接访问一组表,而是为他们提供一个视图。我们可以通过将敏感列从底层查询中排除来防止他们读取这些敏感列。
物化视图
一个物化视图是视图的一种形式,但它也将结果存储到磁盘上。在后续读取物化视图时,返回其结果的时间会比传统视图快得多。这是因为数据对物化视图来说是现成的,而传统视图在每次调用时都要执行底层查询。
使用我们上面的例子,可以这样创建一个物化视图:
1create materialized view transcripts as
2 select
3 students.name,
4 students.type,
5 courses.title,
6 courses.code,
7 grades.result
8 from grades
9 left join students on grades.student_id = students.id
10 left join courses on grades.course_id = courses.id;
从物化视图中读取数据与传统视图相同:
1select * from transcripts;
刷新物化视图
不幸的是,有一个权衡 - 物化视图中的数据并不总是最新的。我们需要定期刷新它,以防止数据变得过于陈旧。要做到这一点:
1refresh materialized view transcripts;
这取决于你如何定期刷新你的物化视图,而且根据每个视图的使用情况,它可能是不同的。
物化的视图与传统的视图
当查询或视图的执行时间太慢时,物化视图是有用的。这些可能发生在涉及多个表和数十亿行的视图或查询中。然而,当使用这样的视图时,应该对数据过期有一定的容忍度。物化视图的一些用例是内部仪表盘和分析。
创建物化视图并不是解决低效查询的方法。即使你正在实现一个物化视图,你也应该始终寻求优化一个运行缓慢的查询。